| Five difficulties and challenges of household energy storage |
| Release time:2023-01-30 08:50:58| Viewed: |
Five difficulties and challenges of household energy storage
The structure of household energy storage system is complex, involving battery, inverter and other equipment. At present, products in the industry are independent from each other, which is easy to cause various problems in actual use, mainly including: complex system installation, difficult operation and maintenance, inefficient use of energy storage batteries and low battery protection level.
1、 System integration: complex installation
Household energy storage is a complex system that combines multiple energy sources and faces ordinary families. Most users want to use it as "household appliances", which puts forward higher requirements for system installation.
At present, the complex and time-consuming installation of household energy storage on the market has become the biggest problem for some users. At present, there are two main schemes of household energy storage system on the market: low pressure energy storage and high pressure energy storage.
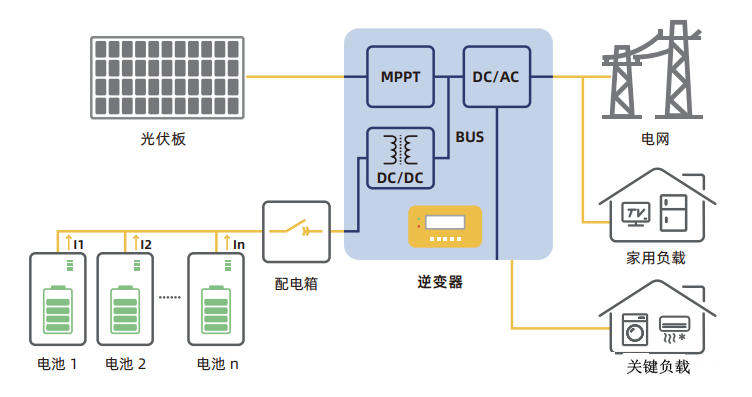
1. Household low-voltage energy storage system (inverter and battery are distributed):
The household low-voltage energy storage system refers to the energy storage system with a battery voltage range of 40~60V, which is connected to the inverter after several batteries are connected in parallel. Through the isolated DC-DC inside the inverter, it is interconnected with the DC output of the photovoltaic MPPT at the bus, and finally converted into AC power through the inverter output. Some inverters have the backup output function.
Figure 1 Household low-voltage energy storage system diagram Main problems of household low-voltage energy storage system:
① Inverters and batteries are separated, heavy equipment and difficult to install;
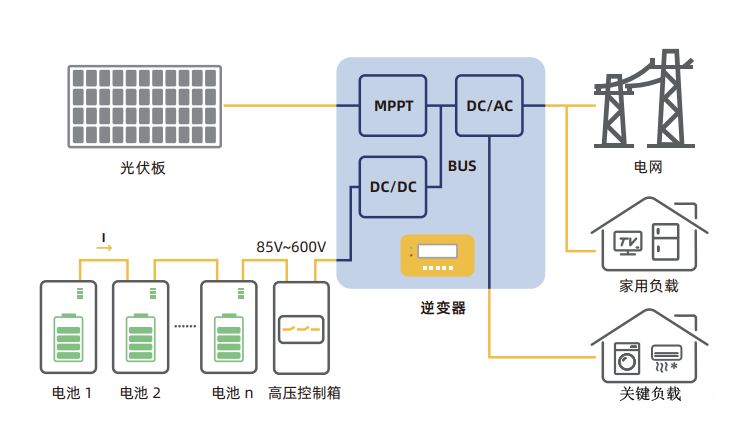
2. Household high-voltage energy storage system:
The battery cluster of the household high-voltage energy storage system adopts a two-level structure, which is output by several battery modules in series through the high-voltage control box. The voltage range is generally 85~600V. The output of the battery cluster is connected to the inverter, which is interconnected with the DC output of the photovoltaic MPPT at the bus through the DC-DC unit inside the inverter, and finally converted into AC power through the inverter output. Some inverters have the backup output function.
Figure 2 Household high-voltage energy storage system diagram Main problems of household high-voltage energy storage system:
In order to avoid using different batches of battery modules directly in series, strict batch management is required in production, delivery, warehouse and installation, which requires a lot of manpower and material resources, and the process will be very cumbersome and complicated, and it will also cause problems for customers to stock;
In addition, the difference between modules will be enlarged due to the self-consumption and capacity attenuation of the battery. The general system needs to be checked before installation. If the difference between modules is large, manual power supply is also required, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
二、 Battery capacity mismatch: capacity loss caused by module difference
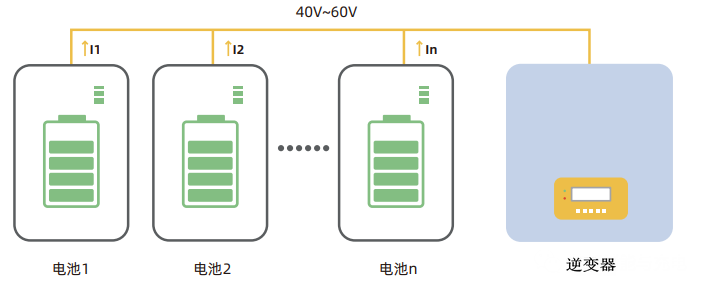
1. Parallel mismatch of household low-voltage energy storage system
Generally, the voltage range of traditional household low-voltage energy storage system is 40~60V, and the capacity expansion is realized through multiple battery packs in parallel. Due to the difference between the cell, module and harness, the charging/discharging current of the battery with high internal resistance is small, and the charging/discharging current of the battery with low internal resistance is large. Some batteries cannot be fully charged/discharged for a long time, which leads to the loss of some capacity of the battery system.
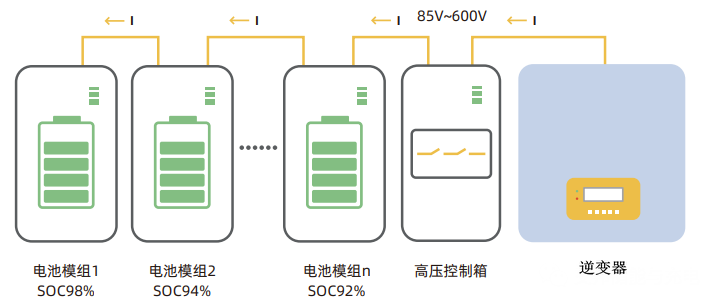
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of parallel mismatch of household low-voltage energy storage system 2. Series mismatch of household high-voltage energy storage system
The general voltage range of household high-voltage energy storage system is 85~600V, and the capacity expansion is realized through multiple battery modules in series. According to the characteristics of the series circuit, the charging and discharging current of each module is the same. However, due to the difference in the module capacity, the battery with small capacity is filled/emptied first, resulting in that some battery modules cannot be filled/emptied for a long time, and some battery cluster capacity is lost.
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of parallel mismatch of household high-voltage energy storage system
三、 Product operation and maintenance: technology and cost threshold are too high
In order to ensure the reliable and safe operation of household energy storage system, one of the effective measures is to do well in operation and maintenance.
However, due to the relatively complex structure of the household high-voltage energy storage system and the high requirements for the professional level of the operation and maintenance personnel, the problems of difficult maintenance, time-consuming and labor-consuming often occur in the actual use process, mainly due to the following two points:
① Regular maintenance requires SOC calibration, capacity calibration or main circuit inspection for the battery pack.
四、 Mixed use of new and old batteries: accelerate the aging and capacity mismatch of new batteries
For the new and old lithium batteries of household low-voltage energy storage system, the internal resistance of the batteries is different, which is easy to cause circulation, and the temperature of the batteries increases, which will accelerate the aging of the new batteries;
For household high-voltage energy storage system, the new and old battery modules are mixed in series. Due to the barrel effect, the new battery module can only be used with the capacity of the old battery module, and the battery cluster will have serious capacity mismatch.
For example, the usable capacity of the new module is 100Ah, and the usable capacity of the old module is 90Ah. If they are mixed, the usable capacity of the battery cluster is only 90Ah. To sum up, it is generally not recommended that new and old lithium batteries be used directly in series or in parallel.
|